Engraving and Milling Machines: Working Principles and Applications
1.What is an Engraving Milling Machine?
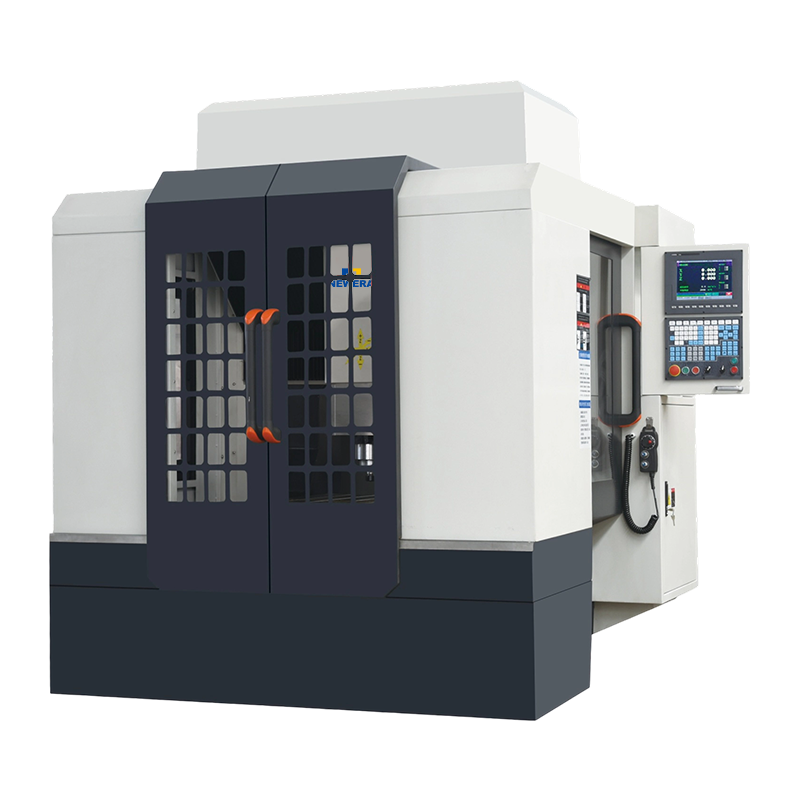
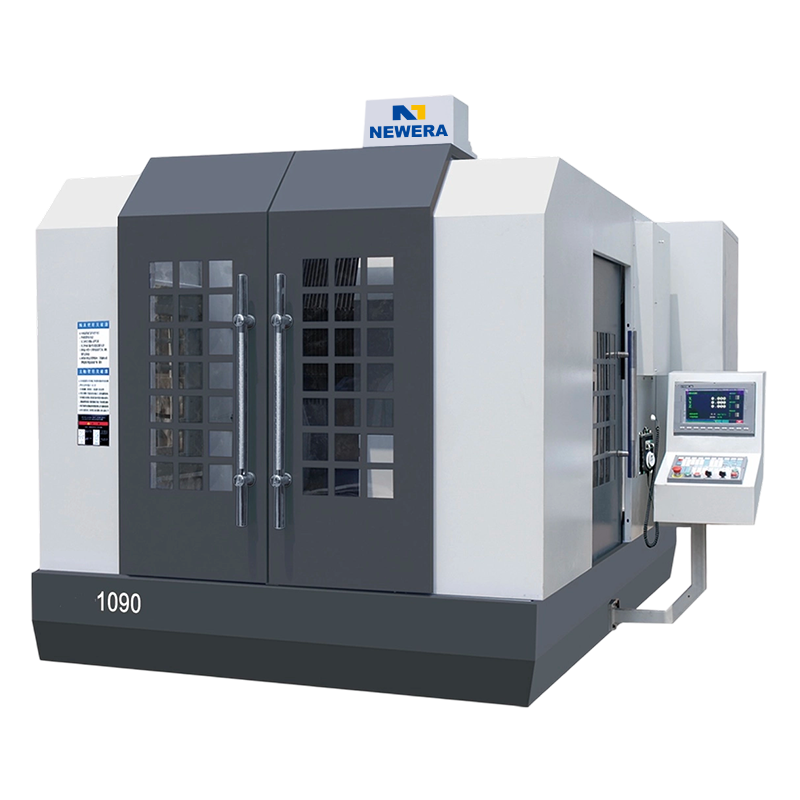
An engraving and milling machine (CNC engraving machine or numerical control engraving and milling machine) is a high-precision device used for processing complex parts and intricate patterns. It is widely used in industries such as machining, mold making, woodworking, metal processing, and artistic engraving. It uses a computer numerical control system to control the cutting tool to cut the workpiece, thereby achieving engraving, milling, and engraving operations on the material surface. Compared to traditional milling machines, engraving and milling machines offer higher precision, richer processing functions, and a more flexible range of applications.
The working principle of an engraving and milling machine is similar to that of a traditional milling machine, mainly using a milling cutter to cut the workpiece. Its core lies in the numerical control system, which controls the movement trajectory of the cutting tool in three-dimensional space according to a preset program to achieve complex engraving and milling tasks. The engraving and milling machine uses CNC technology, utilizing computer-programmed processing path information to precisely control the movement of the milling cutter. The CNC system can handle different processing steps, such as cutting, grooving, and drilling, performing automated processing according to process requirements. Common cutting tools used in engraving milling machines include end mills, ball end mills, and fillet cutters, suitable for various machining methods. These tools contact the workpiece through high-speed rotation, thus performing precision cutting. Unlike traditional milling machines, engraving milling machines can perform more detailed and complex pattern engraving and surface processing, and are widely used in the production of artworks, models, precision molds, furniture, etc.
Main Features of Engraving Milling Machines
(1) High-Precision Machining
Engraving milling machines, controlled by computer numerical control (CNC), can achieve precision down to the micrometer level, enabling them to complete extremely complex and detailed engraving tasks. Their high precision allows them to achieve levels of accuracy unattainable by traditional hand engraving or milling, making them particularly suitable for products requiring precision machining, such as jewelry engraving, automotive parts, and aerospace components.
(2) Flexible Machining Methods
Engraving milling machines have multiple machining functions, enabling milling, engraving, grinding, and other operations to be performed on the same machine. By changing the cutting tools or adjusting the program, engraving milling machines can adapt to the machining needs of different shapes and materials. Furthermore, engraving milling machines excel in three-dimensional machining, capable of handling complex three-dimensional contours.
(3) Automation and High Efficiency
Engraving milling machines are typically equipped with advanced CNC systems, enabling automated processing through programming. This reduces manual intervention and improves efficiency. Operators only need to set the program, and the machine can automatically process materials according to the set parameters, significantly increasing production efficiency.
(4) Adaptability to Various Materials
Engraving milling machines can process a variety of materials, including metals, wood, plastics, stone, and composite materials. Especially in woodworking and carving, they can handle complex carvings and engravings on wood, and even perform high-precision carving on both soft and hard metals.
(5) Reduced Labor Costs
Because engraving milling machines can achieve fully automated operation, reducing manual intervention, labor costs can be significantly reduced during long-term and high-volume production. Furthermore, reduced manual operation also helps improve processing safety.
Although both engraving milling machines and traditional milling machines are CNC machining equipment, they differ significantly in structure, working principle, and application.
(1) Different Control Methods: Traditional milling machines are typically manually controlled by operators. While some high-end traditional milling machines utilize CNC systems, operation still requires significant manual intervention. Engraving milling machines, on the other hand, rely entirely on computer numerical control (CNC) technology. Operators only need to program the settings, and the machine can automatically complete the machining tasks, greatly reducing human error and inefficiency.
(2) Precision and Flexibility: The machining precision of traditional milling machines is usually limited by the operator's experience and skill, making it difficult to achieve the high precision requirements of engraving milling machines. Engraving milling machines, with their powerful CNC functions, can perform precise three-dimensional engraving and detailed machining, suitable for creating complex artistic carvings and high-precision mechanical parts.
(3)Differences in Machining Range: Traditional milling machines are generally suitable for basic two-dimensional machining tasks such as cutting, milling, and drilling, suitable for mass production and machining simple-shaped parts. Engraving milling machines can not only perform traditional milling tasks but also complex operations such as engraving, lettering, and surface treatment, offering greater machining versatility and adaptability.
(4) Adaptability to Processed Materials:Traditional milling machines are typically used to process hard metals, steel, and other relatively robust materials, making them suitable for mass production. Engraving milling machines, on the other hand, can process a wider variety of materials, including soft metals, wood, plastics, and stone, thus finding widespread application in industries such as art carving and furniture manufacturing.
(5) Degree of Automation
While traditional milling machines can be equipped with automation devices such as automatic tool changers and automatic feeding, their overall automation level is low, still requiring considerable manual intervention. Engraving milling machines, however, can achieve almost fully automated operation and can even be adjusted in real-time through remote monitoring, significantly improving production efficiency and processing quality.
With its high precision, multifunctionality, and automation, the engraving milling machine has become an indispensable piece of equipment in modern manufacturing. It has demonstrated enormous potential in fields such as art carving, mold making, and machining. Compared to traditional milling machines, engraving milling machines not only provide more refined processing results but also improve production efficiency and reduce labor costs. With continuous technological advancements, engraving milling machines will play an increasingly important role in more industries.
The following is a comparison table of engraving milling machines and traditional milling machines, distinguishing them from several key dimensions:
| Comparison Dimensions | Engraving Milling Machines | Traditional Milling Machines |
| Machining Objects | Small, precision parts (e.g., molds, reliefs, PCBs) | Medium to large metal parts (e.g., gears, housings, structural components) |
| Machining Accuracy | High (up to ±0.01mm or higher) | Medium (typically around ±0.05mm) |
| Spindle Speed | Ultra-high speed (10,000-60,000 RPM) | Low to medium speed (500-10,000 RPM) |
| Cutting Force | Lower, suitable for light cutting | Higher, suitable for heavy cutting |
| Machine Structure | Lightweight design, fast dynamic response | Heavy-duty structure, high rigidity |
| Control System | Dedicated CNC system, supporting complex path engraving | Ordinary CNC or manual operation |
| Automation Level | High (often integrates automatic tool change and tool setting functions) | Low (manual operation requires frequent intervention) |
| Applicable Materials | Non-metallic (acrylic, wood) or soft metals (aluminum) | Hard metals (steel, cast iron) and high-strength materials |
| Typical Applications | Precision machining of artworks, signage, and electronic products | Rough machining and mass production of industrial parts and molds |
| Price | Mid-to-low-end models have lower costs. | Large-scale equipment has higher prices. |
| Operational complexity | Relies on programming, higher learning curve. | Manual operation is intuitive; CNC models require basic training. |

2.How to Choose the Right Engraving Milling Machine for Your Needs?
Engraving milling machines (CNC engraving machines) are widely used in many industries, such as mold processing, art engraving, and mechanical parts manufacturing. With the continuous development of technology, there are many types of engraving milling machines on the market. Choosing a suitable engraving milling machine is a challenge faced by many enterprises and factories. Selecting an engraving milling machine involves several considerations. This article will provide a detailed introduction from different perspectives on how to choose an engraving milling machine that meets your needs.
(1) Determine Processing Requirements
When choosing an engraving milling machine, you first need to clarify your specific processing requirements. This is the core starting point for selecting an engraving milling machine. Different processing tasks have different requirements for engraving milling machines. First, consider the following factors:
Processing Materials: Engraving milling machines can process workpieces of different materials, such as wood, plastic, metal, and stone. The hardness and cutting characteristics of different materials determine the requirements of the engraving milling machine. For example, wood carving does not require high-end equipment, while metal processing requires more powerful spindle power and higher precision.
Machining Type: Is the machining required for two-dimensional patterns, three-dimensional engraving, or complex multi-axis operations? If it's mainly simple planar milling, a regular three-axis engraving milling machine is sufficient; however, if complex three-dimensional patterns or three-dimensional curved surfaces are required, a multi-axis engraving milling machine is necessary.
Machining Accuracy: If your work involves high-precision machining (such as precision parts, artistic engraving, etc.), you need to choose a more precise engraving milling machine. Accuracy is usually determined by the machine's control system, transmission system, and spindle quality; pay special attention to this when selecting.
(2) Evaluating the Technical Parameters of the Engraving Milling Machine
After clarifying the machining requirements, the next step is to evaluate the technical parameters of the engraving milling machine. These parameters directly determine the equipment's performance and machining capabilities.
Spindle Power and Speed: Spindle power and speed are among the most critical parameters of an engraving milling machine. The higher the power, the higher the hardness of the material the milling machine can cut. Speed affects cutting efficiency and machining quality. Generally, hard metals or heavy workpieces require higher power and speed, while soft materials have lower power requirements. Table Size and Machining Range: The size of the table determines the maximum size of workpieces that the engraving milling machine can handle. If your workpieces are large, you will need to choose an engraving milling machine with a larger table. Furthermore, the machining range of the engraving milling machine must meet your needs, especially in multi-axis machining, where the table's range of motion must be sufficiently large.
Precision and Repeatability: Precision is a key indicator of the engraving milling machine, determining the machining quality. High-precision engraving milling machines can produce more detailed and smoother workpieces. Repeatability affects the stability of multiple machining operations on the same workpiece. Higher precision means higher manufacturing costs, so selection should be based on actual needs.
Control System and User Interface: The control system of the engraving milling machine directly determines the ease of operation and machining flexibility. Common CNC systems include FANUC, Siemens, and Heidenhain, each with its own advantages. Operators should choose a system they are familiar with or find easy to operate. A good user interface and program setting functions can also improve production efficiency.
(3) Consider the Automation Level of the Equipment
The automation level of the engraving milling machine affects production efficiency and ease of operation. Generally, the higher the degree of automation, the more operable the equipment, especially in mass production, which can greatly reduce the time and cost of manual operation.
Automatic Tool Changer: High-end engraving milling machines are usually equipped with an automatic tool changer, which can automatically change tools, thereby reducing manual operation and improving processing efficiency. This is especially important for processing tasks that require frequent tool changes.
Automatic Feeding System: An automatic feeding system can help you reduce manual operation and improve production efficiency, especially in mass production. An automatic feeding system can automatically feed raw materials into the worktable for continuous processing.
Automatic Detection and Adjustment System: Some engraving milling machines are also equipped with an automatic detection system, which can detect processing accuracy in real time and make fine adjustments as needed to ensure the processing accuracy and quality of each workpiece.
(4) Ensuring the Durability and Stability of the Equipment
As equipment used for long periods, the durability and stability of engraving milling machines are crucial. The quality of the equipment determines its service life and long-term processing accuracy.
Machine Tool Materials: High-quality engraving milling machines are usually made of steel or cast iron, which have better rigidity and durability. In contrast, low-quality milling machines may experience vibration and deformation during prolonged operation, affecting machining accuracy and efficiency.
Guideways and Drive Systems: The guideways and drive systems of engraving milling machines need to be highly precise, capable of withstanding heavy loads and maintaining stability over extended periods. High-quality rolling guideways and precision transmission devices significantly improve equipment stability.
Choosing the right engraving milling machine for your needs is not easy. It involves a deep understanding of your machining requirements, precise control of technical parameters, and careful consideration of the equipment brand and after-sales service. By clearly defining your machining needs, evaluating technical parameters, and ensuring equipment stability and durability, you can select the most suitable engraving milling machine to improve production efficiency and machining quality.

3. Common Problems and Solutions for Engraving and Milling Machines
Engraving and milling machines (CNC engraving machines) are widely used in precision machining, artistic engraving, mold making, and other fields. With their high efficiency and high precision, they have become indispensable equipment in modern manufacturing. However, during long-term use, engraving and milling machines may encounter some common problems that can affect machining accuracy and production efficiency. This article will introduce several common problems with engraving and milling machines and provide corresponding solutions to help users troubleshoot problems in a timely manner and ensure the normal operation of the equipment.
(1) Unstable Machining Accuracy
Problem Manifestation: When performing precision machining, the machining accuracy of the workpiece fluctuates, which may lead to increased errors in the finished product, or even complete failure to meet process requirements.
Cause Analysis:
Wear of Mechanical Components: After long-term operation, the spindle, guide rails, lead screws, and other components of the milling machine may wear, leading to unstable movement and affecting machining accuracy.
Control System Problems: Incorrect CNC system or program settings may lead to inaccurate tool paths, affecting the machining accuracy of the workpiece.
Tool Problems: Using worn or unsuitable tools for machining will also lead to a decrease in machining accuracy.
Solutions:
Regularly inspect and replace mechanical components, especially the spindle, guide rails, and lead screw, to avoid accuracy problems caused by wear.
Calibrate the CNC system to ensure accurate program settings and regularly update the software to avoid system failures.
Regularly check the wear of cutting tools and replace severely worn tools promptly; at the same time, select tools suitable for the materials being machined to improve machining accuracy.
(2) Rough or Uneven Machining Surface
Problem Manifestation: The machined surface of the workpiece exhibits obvious roughness or unevenness, resulting in poor surface quality of the finished product, requiring additional processing.
Cause Analysis:
Tool Wear or Improper Tool Selection: Worn tools or the selection of unsuitable tools can lead to uneven cutting and an uneven surface.
Improper Cutting Parameter Settings: Improper settings of parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut can lead to a rough machined surface.
Machine Vibration: Poor equipment stability or insecure clamping can cause vibration, affecting machining quality.
Solutions:
Regularly inspect the cutting tools, replace severely worn tools promptly, and select appropriate tools according to machining requirements. Optimize cutting parameters, adjusting feed rate, spindle speed, and depth of cut to reduce surface roughness.
Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped to avoid vibration during machining and ensure the stability of the milling machine. If necessary, add foundation support or use vibration damping devices.
(3) Tool Breakage or Fracture
Problem Manifestation: During machining, tool breakage or fracture occurs, causing machining interruptions and requiring tool replacement, increasing production costs and downtime.
Cause Analysis:
Excessively Harsh Cutting Conditions: Excessively high cutting speeds or excessive cutting depths may overload the tool, causing breakage or fracture.
Tool Quality Issues: Poor tool quality or selection of tools unsuitable for the material can easily lead to breakage.
Inhomogeneous Workpiece Material: If the workpiece material has uneven hardness, the tool may encounter a sudden increase in cutting resistance during machining, resulting in breakage.
Solutions:
Set cutting parameters appropriately to avoid excessive cutting loads, especially adjusting the spindle speed, feed rate, and depth of cut according to the characteristics of the material being machined.
Select high-quality tools and choose the appropriate tool type based on the hardness of the material being machined.
Check the uniformity of the workpiece material to ensure there are no cracks or impurities before machining, reducing tool load.
(4) Overheating or Spindle Overheating
Problem Manifestation: After prolonged operation, the spindle temperature of the engraving and milling machine rises, even overheating, which may lead to machine shutdown or decreased machining accuracy.
Cause Analysis:
Insufficient Lubrication: Insufficient or expired lubricating oil in the spindle, guide rails, and other components of the milling machine increases friction, generating excessive heat.
Spindle Failure: Damage to the spindle motor or bearings can cause unstable spindle operation, resulting in excessive heat generation.
High Ambient Temperature: High ambient temperature and poor heat dissipation can also easily lead to overheating.
Solutions:
Regularly check and replace the lubricating oil to ensure adequate lubrication of equipment components and reduce heat generated by friction.
Check the operating condition of the spindle motor and bearings, and perform maintenance or replacement as necessary to ensure smooth spindle operation.
Maintain good ventilation around the equipment to ensure the milling machine's cooling system functions properly and avoid prolonged operation in high-temperature environments.
(5) CNC System Failure or Program Error
Problem Manifestation: The CNC system of the engraving and milling machine malfunctions, preventing normal operation or causing program errors, resulting in machining tasks not following the set path.
Cause Analysis:
Control System Hardware Failure: Failure of the circuit board, controller, or power supply may cause the CNC system to malfunction.
Program Input Error: Errors made by the operator when inputting the program, or corruption of the program file, lead to inaccurate machining paths.
Sensor or Encoder Failure: Problems with the equipment's sensors or encoders may cause inaccurate position feedback, affecting the operation of the control system.
Solutions:
Regularly check the hardware of the CNC system to ensure the normal operation of components such as the controller, power supply, and wiring. If hardware failure occurs, repair or replace it promptly.
When inputting the machining program, carefully check its correctness and use automatic checking tools to ensure program accuracy, avoiding input errors.
Regularly check the working status of sensors and encoders to ensure accurate position feedback and avoid inaccurate machining due to equipment failure.
(6) Excessive Equipment Vibration or Noise
Problem Manifestation: During processing, the engraving and milling machine experiences excessive vibration or noise, affecting processing accuracy and potentially impacting the health of operators.
Cause Analysis:
Unstable Machine Foundation: Unstable placement or an unstable foundation can lead to increased vibration.
Loose Components: Loose or damaged connecting components can also cause vibration or noise.
Tool Problems: Improper tool selection or insecure installation can also result in excessive vibration and noise during processing.
Solutions:
Ensure the equipment is installed on a stable surface. Use vibration damping pads or dedicated support devices to increase machine stability.
Regularly inspect all connecting components of the machine to ensure they are secure. Tighten or replace as necessary.
Check that the tools are securely installed. Select appropriate tools and regularly check tool wear to ensure proper functioning.
Engraving milling machines are essential tools for precision machining. While they offer efficient and high-precision machining results, some common problems inevitably arise during long-term use. Understanding these problems and their solutions can help users troubleshoot promptly and ensure efficient equipment operation. Regular maintenance and inspection are key to extending the lifespan of engraving milling machines and improving machining accuracy and production efficiency.
4. Frequently Asked Questions about Engraving Milling Machines
Engraving milling machines (CNC engraving machines) are widely used in mold making, artistic engraving, and mechanical parts processing due to their high efficiency and precision. With their widespread use, users often encounter some problems during daily operation. Understanding common engraving milling machine problems can help you use the equipment better and ensure the machine maintains stable operation.
Q1: What types of processing is an engraving milling machine suitable for?
Answer:
Engraving milling machines are suitable for various types of processing, mainly including the following:
Precision Milling: Engraving milling machines are widely used for processing precision parts, especially suitable for small-batch, high-precision parts production, such as parts processing in the automotive, aerospace, and medical device industries.
Artistic Engraving: Engraving milling machines are often used for artistic engraving on materials such as wood, metal, and plastic, including furniture engraving, jewelry engraving, and the creation of sculptural artworks.
Mold Making: Engraving milling machines can efficiently process complex mold shapes and are widely used in plastic molds, die-casting molds, stamping molds, and other fields.
3D Machining: Engraving milling machines can process complex 3D shapes, suitable for carving intricate three-dimensional patterns or curved surfaces, such as fine artworks or 3D models.
Q2: How do I choose the right engraving milling machine for me?
Answer:
When choosing the right engraving milling machine for you, consider the following factors:
Machining Materials: Different engraving milling machines are suitable for different materials. For example, wood carving generally requires lower power and speed, while harder materials such as metal and stone require higher power and a powerful spindle.
Machining Accuracy: If your machining requirements are very precise, such as mold making and jewelry carving, then you need to choose a high-precision engraving milling machine.
Equipment Functions: Choose whether you need multi-axis functionality based on your machining needs. Three-axis engraving milling machines are suitable for planar machining, while five-axis and above engraving milling machines are suitable for complex 3D carving.
Budget: Choose a cost-effective machine based on your budget. When the budget is tight, you can choose a basic engraving milling machine with a high cost-performance ratio, while for large-scale production or high-precision requirements, it is recommended to choose a more advanced machine.
Q3: What is the difference between an engraving milling machine and a traditional milling machine?
Answer:
The main differences between engraving milling machines and traditional milling machines lie in their control methods, machining accuracy, and applicable scenarios:
Control Method: Engraving milling machines utilize CNC technology, controlling the movement of the cutting tool through a computer program, enabling more complex and precise machining. Traditional milling machines generally rely on manual control or partial CNC, resulting in lower accuracy and flexibility.
Machining Accuracy: Engraving milling machines offer higher accuracy, capable of micron-level machining, making them particularly suitable for high-precision parts, artistic engravings, and the production of complex molds. Traditional milling machines have relatively lower machining accuracy and are suitable for simpler two-dimensional machining tasks.
Machining Flexibility: Engraving milling machines can perform flexible machining in three-dimensional space, adapting to diverse machining needs, while traditional milling machines are mostly limited to two-dimensional or limited three-dimensional machining, with a narrower range of applications.
Q4: What are the common faults of engraving and milling machines?
Answer:
Common faults of engraving and milling machines include:
Unstable machining accuracy: This may be caused by wear and tear of machine tool components, tool problems, or CNC system malfunctions. Regularly inspect mechanical components, ensure the CNC system is operating normally, and replace worn tools promptly.
Tool wear or breakage: Rapid tool wear or breakage may be caused by improper cutting conditions, tool quality issues, or uneven hardness of the processed material. Regularly inspect tools, select appropriate cutting conditions, and use high-quality tools.
Spindle overheating: Spindle overheating may be due to insufficient lubrication, an overheated working environment, or a spindle malfunction. Regularly check the lubrication system and maintain a good working environment to ensure proper spindle cooling.
Excessive equipment vibration or noise: Excessive vibration and noise are usually caused by unstable machine tool foundations, loose components, or unsuitable tools. Check the stability of the equipment, ensure all components are secure, and replace tools with suitable ones as needed.
Q5: How to improve the machining efficiency of an engraving and milling machine?
Answer:
To improve the processing efficiency of a CNC engraving milling machine, you can start from the following aspects:
Optimize cutting parameters: Properly setting parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut can improve processing efficiency and reduce tool wear. For different materials and workpiece shapes, appropriate cutting conditions need to be selected.
Automation functions: If the processing task is complex or mass production is required, you can choose a CNC engraving milling machine equipped with an automatic tool changer and automatic feeding system. This can reduce manual intervention and improve production efficiency.
Regular maintenance and upkeep: Keeping the equipment in good condition, regularly checking the wear of mechanical parts, and replacing aging parts in a timely manner can reduce equipment failures and downtime, thereby improving processing efficiency.
Q6: Is operating a CNC engraving milling machine complicated?
Answer:
Compared to traditional machining equipment, the operation of a CNC engraving milling machine usually has a higher level of automation and digitization. However, the complexity of operation depends on the type and function of the CNC system. Modern CNC engraving milling machines are equipped with user-friendly operating interfaces and programming systems. With some training, operators can quickly master basic operations. In addition, CNC systems usually support graphical programming and automatic path generation, which can greatly simplify the operation. However, for advanced functions (such as multi-axis machining and complex engraving tasks), experienced operators are still required for professional setup.
Q7: What are the maintenance precautions for engraving milling machines?
Answer:
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the long-term stable operation of engraving milling machines. Here are some common maintenance precautions:
Lubrication System: Regularly check and change the lubricating oil to ensure adequate lubrication of all moving parts such as the spindle, guide rails, and lead screws, reducing friction and extending the machine's lifespan.
Equipment Cleaning: Regularly clean the machine tool, especially the worktable, guide rails, and cutting tools, to prevent dust and debris from affecting machining accuracy.
Mechanical Component Inspection: Regularly inspect the wear of mechanical components to ensure the normal operation of components such as guide rails, lead screws, and bearings. Adjust or replace as necessary.
Electrical System Inspection: Regularly inspect the electrical system, including the power supply, control panel, and wiring, to ensure there are no loose connections or malfunctions.
Q8: What is the service life of an engraving milling machine?
Answer:
The service life of an engraving milling machine is generally closely related to the quality of the equipment, frequency of use, and maintenance. Generally, a high-quality engraving milling machine can last for more than 10 years under normal operation and regular maintenance. Low-quality equipment, or equipment used frequently and improperly maintained, may require more frequent repairs and parts replacements, resulting in a relatively shorter lifespan. Proper maintenance, proper operation, and regular upkeep can maximize the lifespan of an engraving milling machine.



 русский
русский عربى
عربى





